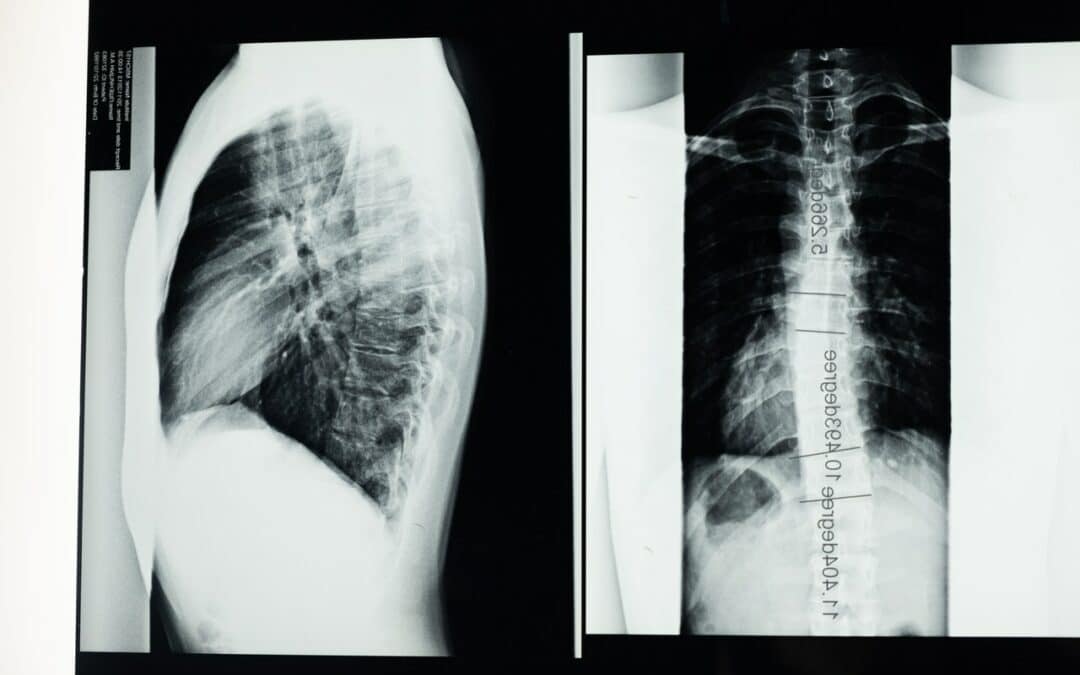
Understanding the Basics of Digital Radiography
In the past, a physical x-ray film would be exposed to the x-ray source, developed, and a metal plate exposed to the developed film. The physical x-ray film would then be developed, and the metal plate would be dipped in a solution and electroplated with metallic toner. This metal would then be placed from one machine to another and from one person to another. The process was very slow and unreliable.
Today, the process relies on the use of a digital x-ray sensor to convert x-rays into digital images. The exposure time is very fast, allowing for the detection of small changes. It also allows for high-quality images. The speed of the machine is also fast.
A standard exposure time for a digital radiography machine is less than a second. The digital radiography machine also has a large memory and high processing capacity. This means that multiple images can be viewed at once, which allows for high-speed diagnosis.
What is Digital Radiography (DR)?
Digital radiography, or DR, is a type of digital radiography that uses a digital detector as part of the imaging system, as opposed to a film-based imaging system. The digital detector is also called a radiographic detector, digital detector, digital detector board, or DD board.
The images produced by DR are then taken, stored, and processed digitally instead of using film, helping to increase the imaging speed, reduce exposure to harmful radiation, and provide a more accurate diagnosis.
What is the Difference Between Digital and Computed Radiography?
Digital radiography, or DR, refers to the use of digital radiographic sensors. These sensors capture the x-ray image and convert it into digital image data that can be stored, processed, and retrieved.
Computed radiography, or CR, is an x-ray imaging technique that uses a computer to process the image data in order to reconstruct the original or a different image.
What are the Advantages of Digital Radiography?
Digital radiography offers a number of benefits, including capturing picture detail more accurately, reducing exposure to harmful radiation, and providing a more accurate diagnosis. In addition to that, digital radiography also revolutionizes the field by providing the following advantages:
- Shorter exposure times;
- Real-time applications;
- Use of analysis tool and defect-recognition software;
- Improved detail detectability;
- Enhanced SNR and linearity;
- Reduced inspection time;
- Safer for the environment;
- Digital image enhancement and data storage;
- Higher productivity;
- Portability;
- Increased dynamic range enables multiple thickness to be inspected in one shot;
- Immediate feedback;
- Easy to transfer to customers electronically;
- Accurate imaging;
What are the Different Applications of Digital Radiography?
Digital radiography is used today in many different industries, including dentistry, veterinary, aerospace, engineering, chemical, and many more.
The Bottom Line: The Many Wonders of Digital Radiography
The digital radiography machine is a versatile and reliable device that keeps us safe from harmful x-rays. Digital radiography is also called digital radiography and radiography. It is also a non-invasive imaging system that is used to detect defects in a wide range of equipment.
With that in mind, it’s safe to say that digital radiography is considered to be the next generation of radiography.
How Can We Help You?
Are you looking for a chiropractic clinic? Kindspine can help you. We focus on performing chiropractic practices to help alleviate pains in your body through upper cervical chiropractic methods. This addresses migraines, headaches, and more. Book an appointment with us today!